What is a Lateral Line?
The Lateral Line is a sense organ located on the side of a fish that allows them to detect movement in the water. This helps them out when it comes to finding food, avoiding predators, and staying in line with their friends when they move in big schools. Some fish have a more developed lateral line than others do, and even some amphibians have developed a lateral sense!
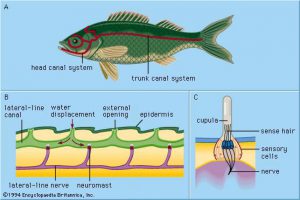
How exactly does the Lateral Line work?
I’m glad you asked! The lateral line gets information through these cool receptor patches called neuromasts, located right under the scales of the lateral line in fluid filled canals. The message reception occurs within small hair cells or cilia, which are present in all vertebrate ears, even our own! Water movement or pressure stimulates these cells and help the fish gain a sense of its position in the water.

Can we see this line on a fish?
Yes we can! This organ is made up of a long line of scales spanning from the head right around the gill slits to the tail located on either side of the fish. The lateral line usually looks like a faint stripe, but underneath those scales is a complex sensory organ that can interpret electrical impulses from the water and alert the fish of its surroundings and changes in the water.
 Do we have something similar to a Lateral Line?
Do we have something similar to a Lateral Line?
We don’t exactly have the ability to detect electrical impulses in the space around us, but we certainly have some pretty functional senses! Do you ever catch your friends trying to sneak up on you because you can sense them coming? The lateral line might feel similar to us if we combined our sense of hearing, vision, and other sensory feelings. Might be nice to have something like that!

The Lateral Line sounds great, where can I get one?!
Well, it would help to grow some scales, fins, and become a fish. Then you could really get your schooling on!


